A. 九进制转十进制
分析
直接手算即可,就不编程了,答案 为
B. 顺子日期
分析
此题目前有有争议,题意没有交代清楚如 012 算不算顺子。
本人考虑的是 012 计算在内的。前面 2022 肯定无法接后面 34 这个月份构成顺子,则直接枚举每一个月每一天即可,之后判断月份和日期构成的 mmdd 格式是否存在顺子即可。此外,2022显然不是闰年,二月不用+1。
答案:14
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int ms[13] = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int main() {
int s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= ms[i]; j++) {
char t[10];
sprintf(t, "%02d%02d", i, j);
if (t[0] + 1 == t[1] && t[1] + 1 == t[2]) {
s++;
continue;
}
if (t[1] + 1 == t[2] && t[2] + 1 == t[3]) s++;
}
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
C. 刷题统计
分析
模拟
直接计算其需要多少完整的周,之后判断剩下的几天内可以完成。
代码
- 已过100%用例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL a, b, n;
int main() {
cin >> a >> b >> n;
LL week = a * 5 + b * 2;
LL m = n / week;
LL s = m * 7;
LL res = n % week;
if (res == 0) {
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
int i = 1;
for (; i <= 7; i++) {
LL d = i >= 6 ? b : a;
res -= d;
if (res <= 0) break;
}
cout << s + i << endl;
return 0;
}
D. 修剪灌木
分析
模拟,数学
当第 棵数被修剪后,若当前方向向右,则向右走 天,再倒回来,走 天回到第 棵树的位置,则两次修剪第 棵树间隔了 天,同时,期间树木长高到最高了 ;同理,若再往左边走,两次修剪间隔 天,期间树木长高到最高 。比较两个方向的最高高度即为第 棵树的最大高度。
代码
- 已过100%用例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d\n", max(n - i, i - 1) * 2);
}
return 0;
}
E. X 进制减法
分析
模拟
每个进制位由低一位的位决定,每个进制尽量取较小的(>=2)。
代码
- 已过100%用例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
typedef long long LL;
vector<int> a, b;
int n, ma, mb;
int main() {
cin >> n >> ma;
for (int i = 0, x; i < ma; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);
a.push_back(x);
}
cin >> mb;
for (int i = 0, x; i < mb; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);
b.push_back(x);
}
//从低位到高位
reverse(a.begin(), a.end());
reverse(b.begin(), b.end());
LL pre = 0; //前面几位的值
for (int i = ma - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
LL t = pre + a[i];
if (mb > i) t -= b[i];
t = (t + MOD) % MOD;
if (i == 0) {
pre = t;
break;
}
//i > 0,当前位置需乘上后一位的进制,为后一位两个数中最大值 + 1
int mx = a[i - 1];
if (mb > i - 1) mx = max(mx, b[i - 1]);
pre = t * max(2, mx + 1) % MOD;
}
cout << pre << endl;
return 0;
}
F. 统计子矩阵
分析
前缀和,双指针
统计矩阵前缀和,用 表示 以 为左上角, 为右下角的矩阵内的节点和。
之后枚举子矩阵的上下限 ,再利用双指针从左往右扫一趟累加满足条件的子矩阵左右两边即可。
代码
- 已过100%用例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 510;
int m, n, k;
int s[N][N], ts[N];
//s[j][i] 表示第 j 列的 1-i 行前缀和
//C语言网要用快读,不然会被卡
template<typename T>
void read(T &x) {
x = 0;
T f = 1;
char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = -1;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
x = f * x;
}
int main() {
// cin >> m >> n >> k;
read(m), read(n), read(k);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
// scanf("%d", &s[j][i]);
read(s[j][i]);
s[j][i] += s[j][i - 1];
}
}
LL ans = 0;
for (int r1 = 1; r1 <= m; r1++) { //上边距
for (int r2 = r1; r2 <= m; r2++) { //下边距
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { //计算限定上下界的第 j 列的元素和
ts[j] = s[j][r2] - s[j][r1 - 1];
}
int ss = 0; //表示[L, R-1]的前缀和,若 L == R则为0
//枚举并累加以 R 为右端点且满足条件的区间
for (int L = 1, R = 1; R <= n;) { //L,R双指针从左往右扫描
int t = ts[R]; //限定上下边的情况,当前第R列的和
if (ss + t <= k) { //限定上下边的情况,若当前 [l, R-1] 区间内的和加上第 R 列满足条件
ans += (R - L + 1); //则以 L 到 R 为左端点,R 为右端点的子区间都满足条件,更新答案
ss += t;
R++;
} else { //不满足条件,左指针右移,缩小区间,即减小区间和
ss -= ts[L];
if (++L == R + 1) { //若超过右指针,则说明 R 这一列的和都大于 k,右指针向右移动更新
ss = 0;
R++; //更新后 L == R
}
}
}
}
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
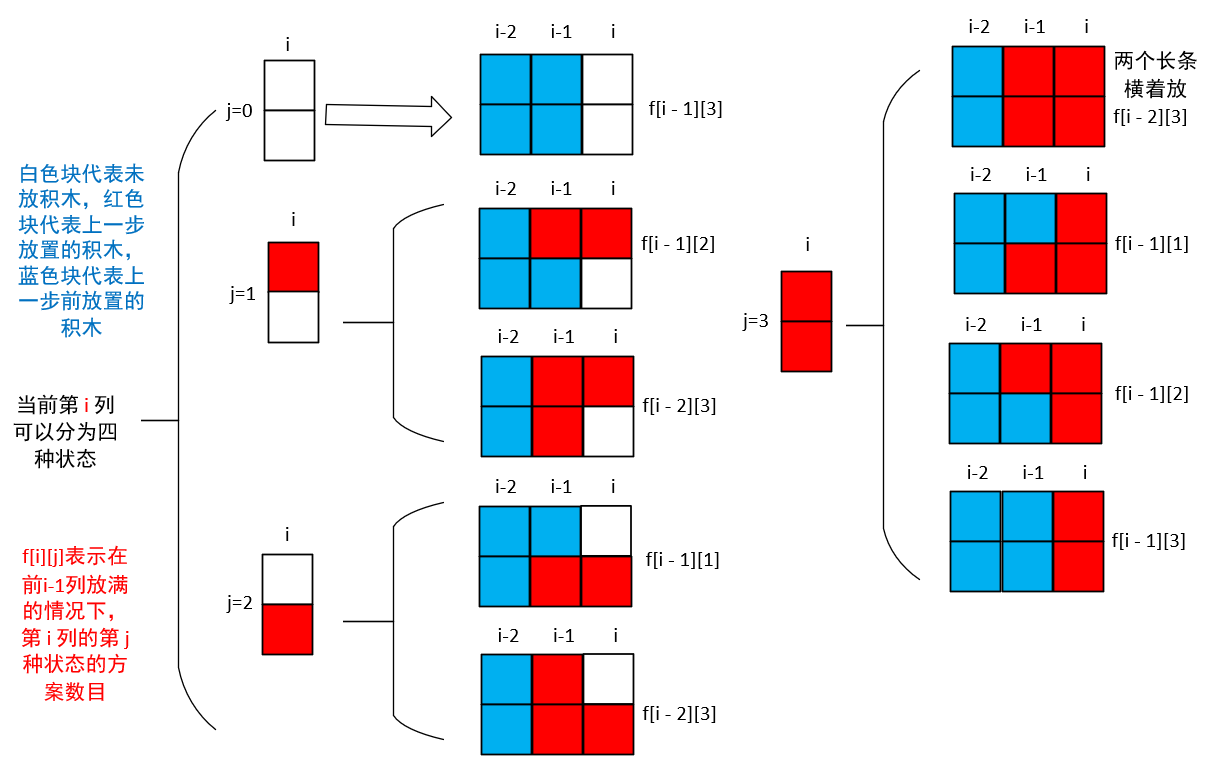
G. 积木画
分析
动态规划
见下图。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define gcd __gcd
#define fir(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define rif(i, b, a) for(int i = b; i >= a; i--)
#define sync ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define pl (p << 1)
#define pr (p << 1 | 1)
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e7 + 5, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int n, f[N][4];
int main(){
cin >> n;
f[0][3] = 1;
fir(i, 1, n) {
f[i][0] = f[i - 1][3];
f[i][1] = f[i - 1][2];
if(i >= 2) {
f[i][1] = (f[i][1] + f[i - 2][3]) % MOD;
}
f[i][2] = f[i - 1][1];
if(i >= 2) {
f[i][2] = (f[i][2] + f[i - 2][3]) % MOD;
}
f[i][3] = (f[i - 1][1] + f[i - 1][2]) % MOD;
f[i][3] = (f[i][3] + f[i - 1][3]) % MOD;
if(i >= 2) {
f[i][3] = (f[i][3] + f[i - 2][3]) % MOD;
}
}
cout << f[n][3] << endl;
return 0;
}
H. 扫雷
分析
bfs, dfs
见代码!
代码
- 已过100% 用例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e4 + 5, MAXN = 1e9;
bool v[N];
struct P {
int x, y, r, cnt;
} p[N];
unordered_map<LL, int> mp;
int n, m, s, tot;
//hash坐标,x 和 y 在 [0, 1e9] 共有 1e9 + 1 种取值
inline LL get(LL x, LL y) {
return x * (MAXN + 1) + y;
}
void bfs(int k) {
queue<int> qu; //队列存放有雷的坐标点的下标
qu.push(k);
while (qu.size()) {
int u = qu.front();
qu.pop();
LL dr = 1LL * p[u].r * p[u].r;
//在当前坐标点爆炸后的爆炸范围内搜索是否存在未引爆的点
//遍历横坐标,注意题目保证 x 和 y 在 [0,1e9] 范围内
for (int x = max(0, p[u].x - p[u].r); x <= p[u].x + p[u].r && x <= MAXN; x++) {
LL dx = 1LL * (x - p[u].x) * (x - p[u].x);
//向上遍历纵坐标
for (int y = p[u].y; 1LL * (y - p[u].y) * (y - p[u].y) + dx <= dr && y <= MAXN; y++) {
LL id = get(x, y);
if (mp.find(id) == mp.end()) continue; //该坐标不存在雷,跳过
int index = mp[id];
if (v[index]) continue; //该坐标已经访问过,跳过
qu.push(index); //该坐标背引爆,加入对列,后续查找其能引爆的雷
s += p[index].cnt; //答案更新
v[index] = true; //标记该坐标点为已经引爆
}
//向下遍历纵坐标
for (int y = p[u].y - 1; 1LL * (y - p[u].y) * (y - p[u].y) + dx <= dr && y >= 0; y--) {
LL id = get(x, y);
if (mp.find(id) == mp.end()) continue;
int index = mp[id];
if (v[index]) continue;
qu.push(index);
s += p[index].cnt;
v[index] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1, x, y, r; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &r);
//将其坐标和下标放到map,方便后面枚举坐标时,能快速找到是否存在对应的雷
LL id = get(x, y);
if (mp.find(id) != mp.end()) { //该坐标存在雷,则更新
int index = mp[id]; //坐标对应的下标
if (p[index].r < r) p[index].r = r; //取该点的最大半径,能引爆更多的雷
p[index].cnt++; //当前坐标点的雷的数量增加
} else {
mp[id] = ++tot;
p[tot] = {x, y, r, 1};
}
}
for (int i = 1, x, y, r; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &r);
p[tot + 1] = {x, y, r, 0}; //放在最末尾
bfs(tot + 1); //计算从当前点引爆能引爆的雷的数量
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
I. 李白打酒加强版
分析
动态规划
代码中写的很清楚!
代码
- 暴力骗分,40%样例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
LL s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << (m + n); i++) { //枚举每种方案,1为酒馆,0为花
if (i & 1) continue; //若最后一个不为花 ,则不为合法方案,跳过
int cn = 0; //统计该序列中遇到酒馆的次数
for (int j = 0; j < m + n; j++) {
if (i >> j & 1) cn++;
}
if (cn != n) continue; //如果酒馆次数不等于目标次数,跳过
LL t = 2; //当前酒的斗数
bool f = true;
for (int j = m + n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i >> j & 1) t *= 2;
else {
if (--t == -1) { //若为0且遇到花店,为不合法方案
f = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (f && t == 0) s++;
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
- DP,100%样例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m, f[N][N][N];
LL s;
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
f[0][0][2] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
if (i == n && j == m) { //最后特判,结尾遇到花,只能从f[n][m - 1][1]转移过来
f[i][j][0] = f[i][j - 1][1];
break;
}
for (int k = 0; k <= m; k++) { //酒最多 m 斗,否则就算接下来全部 m 次花,都不能到达0的状态。
//1.遇到花店得到的
if (j && k < m) f[i][j][k] = (f[i][j][k] + f[i][j - 1][k + 1]) % MOD;
//2.遇到酒馆得到的,注意这里酒是加倍,则一定是偶数状态才转移过来了
if (i && k % 2 == 0) f[i][j][k] = (f[i][j][k] + f[i - 1][j][k / 2]) % MOD;
}
}
}
cout << f[n][m][0] << endl;
return 0;
}
J. 砍竹子
分析
模拟
先给出两个输入样例,第一个样例是官方的,第二个是自己乱造的。
样例1
6
2 1 4 2 6 7
样例2
10
20 22 30 40 42 50 60 70 80 2222
对于上图的两个输入样例分别如下:

首先,对于每个高度(),其最多可以被砍掉六次变为 1。
我们将每颗竹子执行砍操作直到变为1,得到结果如上图所示。可以看到,在对应的每列连续相同的高度的竹子(用同一个框框起来)可以一起被砍掉,最后的结果即为画的框的数量。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sync ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr)
#define frein freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin)
#define gcd __gcd
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define fir(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define rif(i, b, a) for(int i = b; i >= a; i--)
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define pl (p << 1)
#define pr (p << 1 | 1)
#define hmid(l, r) ((l + r) >> 1)
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int n;
vector<LL> g[N];
inline LL cutdown(LL x) {
return (LL) sqrt((x >> 1) + 1);
}
int main() {
// frein;
cin >> n;
LL x;
fir(i, 1, n) {
scanf("%lld", &x);
g[i].pb(x);
while (x > 1) {
x = cutdown(x);
g[i].pb(x);
}
reverse(g[i].begin(), g[i].end());
}
int tot = 0;
fir(j, 1, 6) {
LL pre = 0;
fir(i, 1, n) {
if (j < int(g[i].size())) {
if (pre == 0) {
tot++;
pre = g[i][j];
} else if (pre != g[i][j]) {
tot++;
pre = g[i][j];
}
} else if (pre) pre = 0;
}
}
cout << tot << endl;
return 0;
}